Better sleep, calmer mind, sharper focus, can L-theanine really deliver it all?
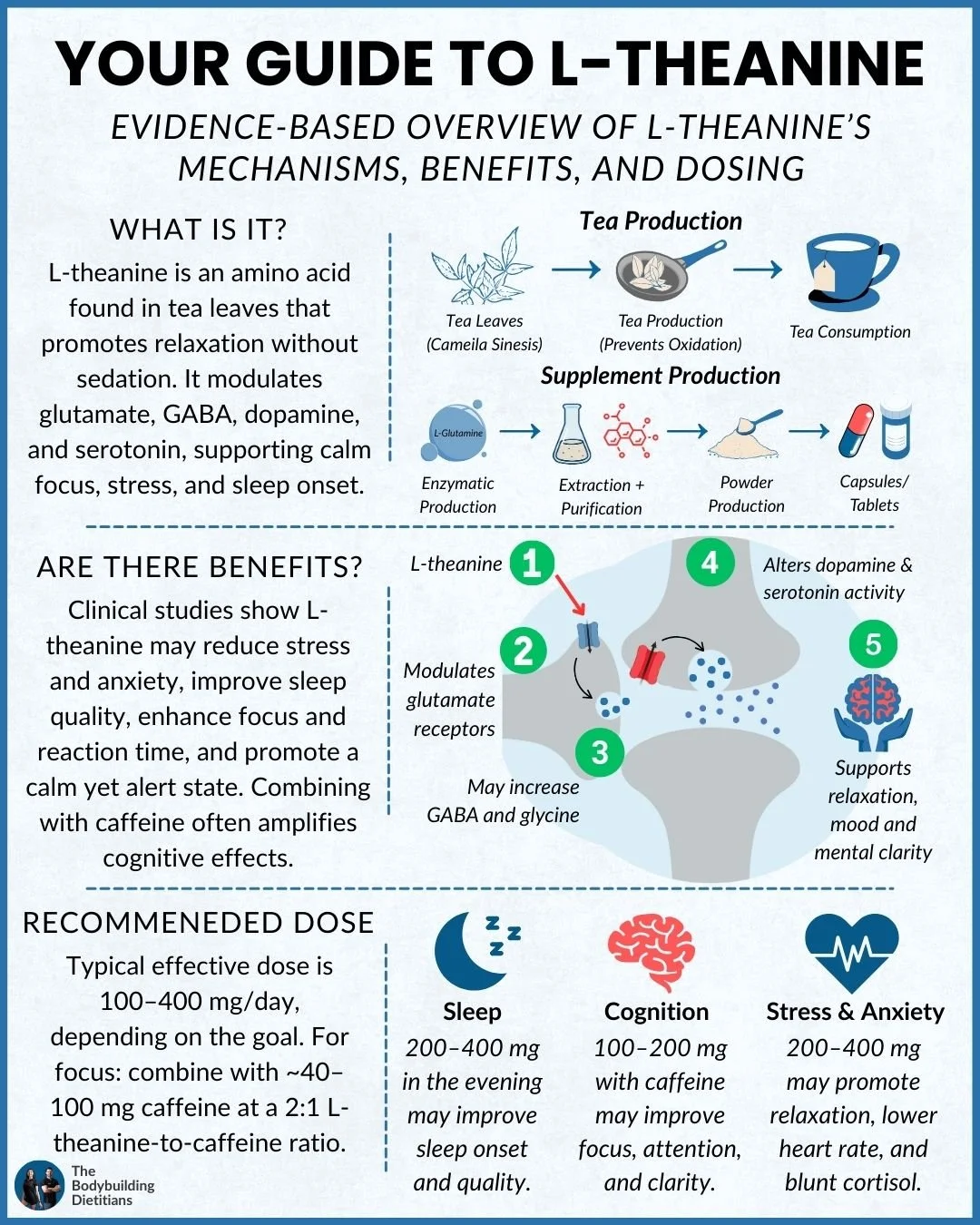
L-theanine is a naturally occurring amino acid found primarily in tea leaves (Camellia sinensis). Known for promoting relaxation without sedation, it has attracted growing interest from both the scientific community and the general public for its potential to support mental clarity, stress resilience, and sleep quality. Unlike many calming agents, L-theanine appears to enhance a state of “relaxed alertness”, promoting mental calm while preserving reaction time and attentional performance.
Mechanisms of Action
Once ingested, L-theanine readily crosses the blood–brain barrier, where it influences several neurotransmitter systems:
Glutamate modulation: L-theanine interacts with glutamate receptors, dampening excessive excitatory signalling that can contribute to stress and mental overactivity.
GABA, dopamine, and serotonin enhancement: Research suggests it can increase levels of these neurotransmitters, which are closely tied to mood regulation, relaxation, and focus.
Alpha brain wave activity: EEG studies indicate L-theanine increases alpha frequency brain waves, often associated with a calm but alert mental state.
This multi-pathway modulation provides the neurochemical foundation for its observed effects on stress, cognition, and sleep.
Sleep
L-theanine is not a sedative, yet it may improve sleep quality by making it easier to transition into a restful state. Research suggests doses of 200–400 mg in the evening may:
Reduce sleep latency (the time taken to fall asleep)
Increase time spent in restorative stages of sleep
Improve overall sleep satisfaction, particularly in individuals whose sleep is disrupted by stress or an overactive mind
It’s important to note that L-theanine will not override poor sleep hygiene or treat clinical insomnia in isolation, behavioural changes and good sleep practices remain essential.
Stress Reduction and Calm Focus
Several controlled studies have found that L-theanine can lower subjective stress levels and physiological stress markers, including heart rate and salivary cortisol, during acute stress challenges.
This effect is subtle but meaningful, often described as creating a state of “calm concentration” rather than sedation. The ability to remain relaxed while mentally alert makes it a useful adjunct for activities that require sustained focus under pressure, from study sessions to athletic performance.
Cognition and Performance
When taken alone, L-theanine offers modest but measurable improvements in attention, working memory, and reaction time. However, its synergy with caffeine is where it truly shines:
Improved focus and accuracy
Faster reaction times
Reduced mental fatigue
Lower perceived jitteriness compared to caffeine alone
This combination may explain why green tea often produces a smoother, more sustained alertness compared to coffee. The most common pairing in research uses a 2:1 L-theanine to caffeine ratio, such as 200 mg L-theanine with 100 mg caffeine.
Recommended Dosing
Research suggests effective doses range from 100–400 mg/day, depending on the intended outcome:
Sleep: 200–400 mg in the evening
Cognition: 100–200 mg with ~40–100 mg caffeine (2:1 ratio)
Stress and anxiety: 200–400 mg spread across the day
Individual responses vary, and like any supplement, L-theanine should be viewed as complementary to, not a substitute for, foundational lifestyle habits such as quality sleep, regular exercise, balanced nutrition, and effective stress management.
Key Takeaways
L-theanine promotes relaxation without sedation, potentially improving sleep quality, reducing stress, and enhancing focus.
Its effects are mediated through neurotransmitter modulation and increased alpha brain wave activity.
Combining L-theanine with caffeine appears to offer synergistic benefits for mental performance with fewer side effects.
Optimal results come from pairing supplementation with good sleep hygiene, nutrition, and stress-management practices.